In the world of sports, the pursuit of excellence often pushes athletes to the limits of their physical capabilities. While hard work, dedication, and natural talent are traditionally considered the …
The Hidden Opponents: Doping and PED’s in the Sports Arena
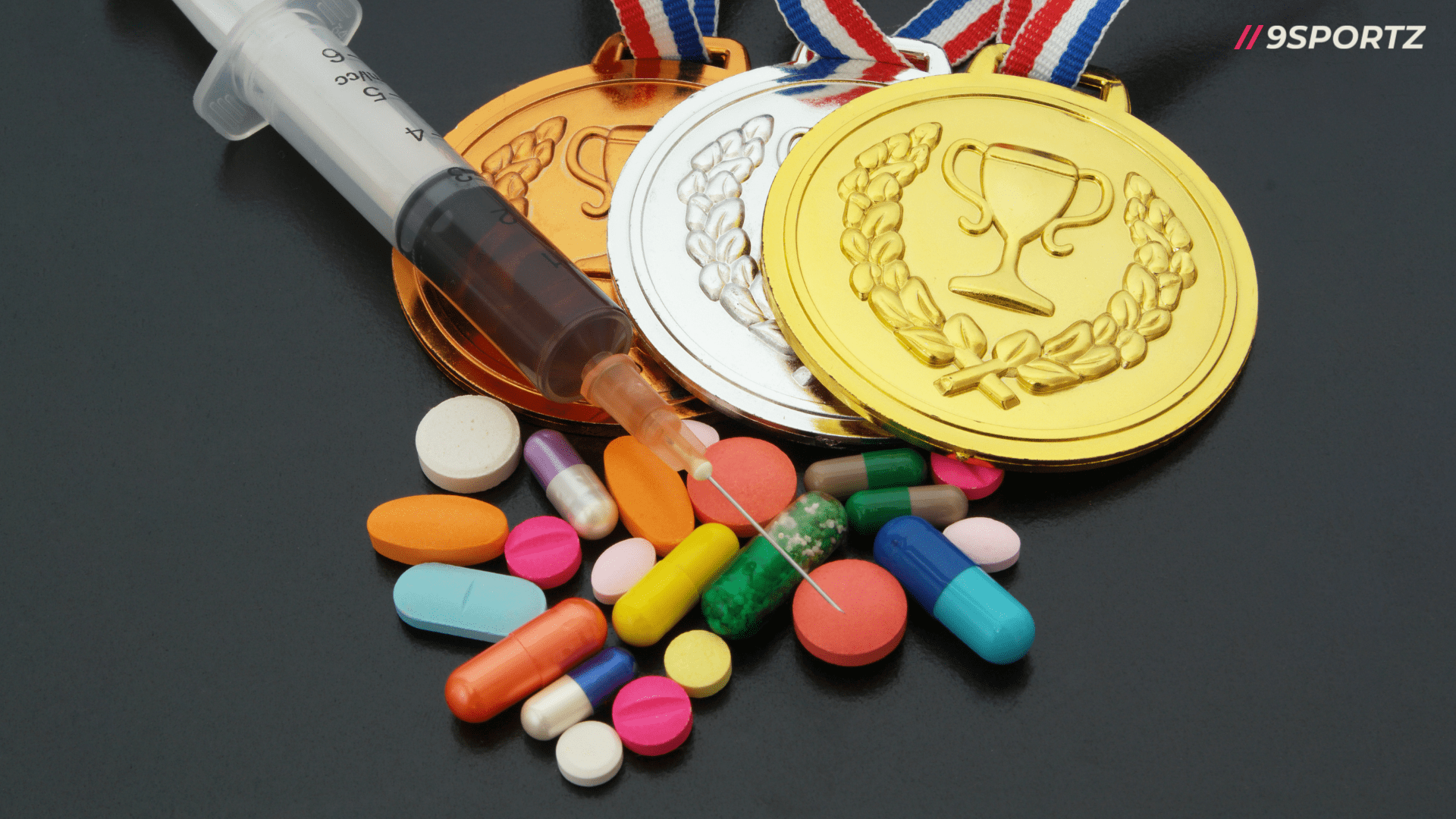
In the world of sports, the pursuit of excellence often pushes athletes to the limits of their physical capabilities. While hard work, dedication, and natural talent are traditionally considered the pillars of athletic success, there exists a darker side characterized by the use of performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs) and doping. This article delves into the intricate web of doping in sports, exploring its history, prevalence across different sports, legal implications, types of drugs used, effects on athletes, controversies, anti-doping measures, ethical considerations, and the future landscape of clean sports.
Introduction to Doping and Performance Enhancing Drugs (PEDs)
Doping refers to the use of banned substances or methods by athletes to gain a competitive advantage. These substances, commonly known as performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs), can significantly enhance an athlete’s strength, speed, endurance, or recovery rate beyond what is naturally achievable.
History of Doping in Sports
The use of performance-enhancing substances dates back centuries, with early instances documented in ancient Greek and Roman athletic competitions. However, the modern era of doping in sports gained momentum in the mid-20th century with the advent of synthetic steroids and other potent drugs.

Popular Sports and Doping
Doping is prevalent in a wide range of sports, from endurance-based disciplines like cycling and marathon running to strength-dependent sports like weightlifting and powerlifting. However, no sport is immune. From archery to yachting and all sports in between, athletes have sought out drugs to improve their performance or hasten recovery from injury. The motivations behind doping vary across different sports, influenced by factors such as prize money, prestige, and the intense pressure to succeed.
Legality and Regulation
The use of PEDs to enhance performance is considered unethical and is prohibited by most international sports organizations. To combat doping, international sports organizations, such as the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), have implemented strict regulations and testing protocols. Athletes caught using banned substances face severe consequences, including suspension, loss of medals, and damage to their reputation. However, there is generally no criminal liability for an athlete who uses doping or substances banned in sports.

Usage of Doping and PEDs in Sports
PEDs have the ability or potential to drastically alter the human body and biological functions, including the ability to considerably improve athletic performance in certain instances. These drugs, however, can be extremely dangerous and, in certain situations, deadly. The primary medical use of some of these compounds, such as anabolic agents, is to treat delayed puberty, some types of impotence, and wasting of the body caused by HIV infection or other muscle-wasting diseases.
Types of Performance Enhancing Drugs
Performance-enhancing drugs encompass a diverse array of substances, including anabolic steroids, stimulants, and blood doping techniques. These drugs can have profound effects on the body, altering hormone levels, increasing muscle mass, and boosting oxygen-carrying capacity.
Effects of Doping on Athletes
While PEDs may offer short-term performance gains, they also pose significant health risks and long-term consequences for athletes. The use of PEDs can have both physiological and psychological side effects. Physiological side effects can include acne, male pattern baldness, liver damage, premature closure of the growth centers of long bones (in adolescents) which may result in stunted growth.
Psychological side effects can include increased aggressiveness and sexual appetite, sometimes resulting in abnormal sexual and criminal behavior, often referred to as “Roid Rage”. Withdrawal from anabolic steroid use can be associated with depression, and in some cases, suicide.
Controversies and Scandals
The history of sports is riddled with doping scandals that have tarnished the reputations of athletes and cast a shadow over entire sports federations. High-profile cases, such as the Lance Armstrong doping saga in cycling and the Russian doping scandal in track and field, have exposed the widespread prevalence of doping and the challenges of enforcement. Another infamous scandal include the East German government dosing its athletes with performance-enhancing drugs in the 1970s and ’80s, and the case of British cyclist Tom Simpson, who died during the Tour de France in 1967 due to the use of amphetamines.

Statistical Data
– In 2020, the number of anti-doping rule violations worldwide totaled 910¹. Athletics and cycling recorded the most anti-doping rule violations worldwide in 2020, accounting for around 16% and 14% of the violations respectively¹.
– From 2003 to 2008, 1-3% of tested athletes were found to use PEDs. Among elite athletes, this number rises to 14-39%.
– In 2018, anabolic steroids accounted for 49% of reported adverse findings by the World Anti Doping Agency (WADA).
– According to Statistica, the number of anti-doping rule violations worldwide from 2013 to 2019 ranged from 1,595 to 1,953.
– The regulatory bodies for sports have reported rates ranging from 5% to 31% for the use of performance-enhancing substances among athletes
Source: Statista.com | Physio-pedia.com | Invigormedical.com | gitnux.org
Anti-Doping Measures
Anti-doping efforts rely on a combination of testing procedures, intelligence gathering, and educational programs aimed at deterring athletes from using banned substances. Despite advancements in testing technology, staying one step ahead of doping remains a perpetual cat-and-mouse game.
Ethical Considerations
The use of performance-enhancing drugs raises complex ethical questions regarding fairness, integrity, and the essence of sport. While some argue that doping undermines the principles of fair play and jeopardizes athletes’ health, others contend that it is an inevitable consequence of the relentless pursuit of excellence.
Future of Anti-Doping Efforts
The future of anti-doping efforts lies in technological innovations, collaborative initiatives between stakeholders, and a renewed emphasis on education and prevention. As doping methods evolve, so too must the strategies employed to detect and deter them.
Education and Awareness
Building a culture of clean sports requires the collective efforts of athletes, coaches, administrators, and fans. Educating athletes about the risks and consequences of doping, promoting ethical behavior, and fostering a supportive environment are essential steps in safeguarding the integrity of sports.
Rehabilitation and Support for Doped Athletes
For athletes who have fallen prey to doping, rehabilitation and support programs offer a pathway to redemption and recovery. These programs address not only the physical effects of doping but also the psychological toll of facing bans and public scrutiny.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
The portrayal of doping in the media plays a crucial role in shaping public perception and influencing policy decisions. Responsible reporting, balanced analysis, and transparency are essential to fostering informed discussions about doping and its impact on sports.
Conclusion
In conclusion, doping remains a persistent challenge in the world of sports, posing threats to the health of athletes, the integrity of competitions, and the values that underpin sportsmanship. While anti-doping efforts have made significant strides, the battle against doping is far from over. It requires the collective commitment of athletes, administrators, policymakers, and fans to uphold the spirit of fair play and ensure that sports remain a beacon of inspiration and excellence.
Frequently Asked Question’s
- How widespread is doping in professional sports?
Doping exists in various forms across a wide spectrum of sports, although its prevalence varies depending on factors such as the level of competition and the effectiveness of anti-doping measures.
- What are some common signs that an athlete may be using performance-enhancing drugs?
Signs of doping can include rapid muscle gain, unusual changes in physical appearance, sudden improvements in performance, and erratic behavior.
-
Are all performance-enhancing drugs illegal?
While many performance-enhancing drugs are banned by sports organizations, some substances are permitted for medical use under certain circumstances. It’s essential for athletes to familiarize themselves with the rules and regulations governing drug use in their respective sports.
- How do anti-doping agencies detect banned substances in athletes’ bodies?
Anti-doping agencies employ various testing methods, including urine and blood tests, to detect traces of banned substances in athletes’ samples. These tests are continuously updated and refined to keep pace with emerging doping techniques.
- What can fans do to support clean sports and discourage doping?
Fans play a crucial role in promoting clean sports by holding athletes, teams, and sports organizations accountable for their actions. Supporting athletes who compete with integrity and advocating for stricter anti-doping measures can help create a culture of fair play and sportsmanship.
Follow us for more sports news and updates on –